Ectopic Pregnancy
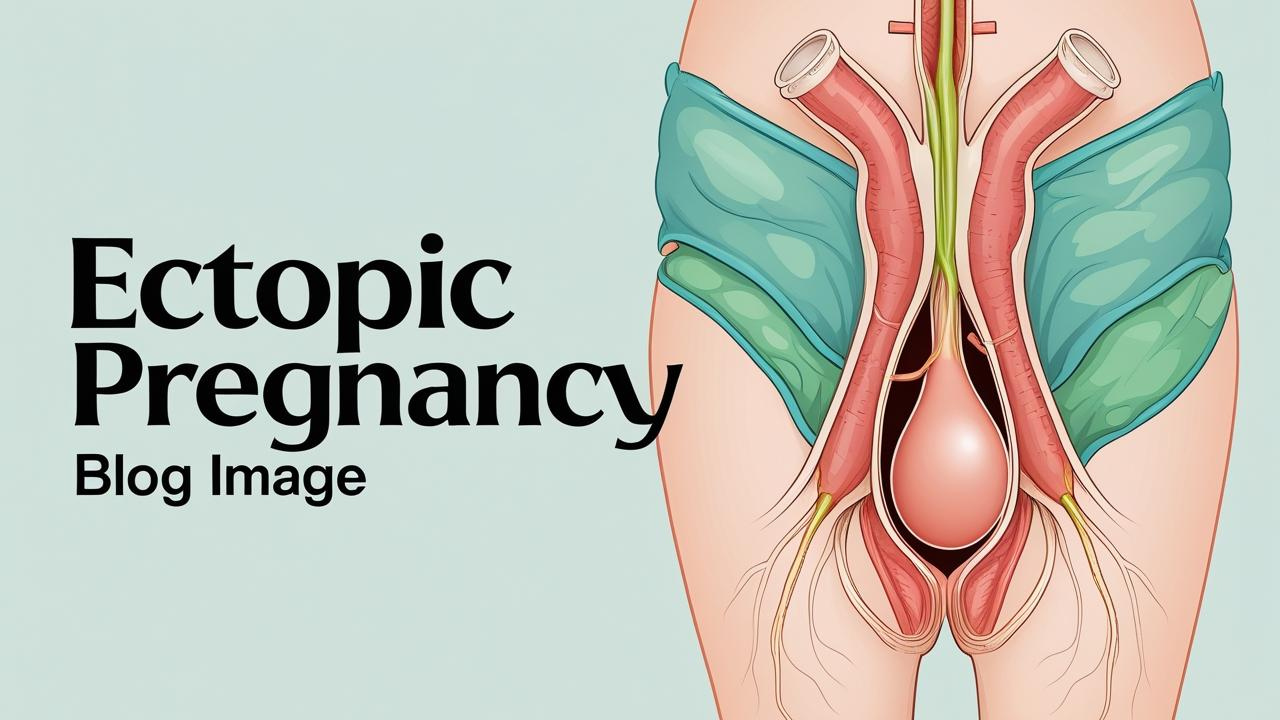
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, usually in a fallopian tube. This condition is also known as a tubal pregnancy.
Unfortunately, an ectopic pregnancy cannot survive, and if left untreated, it can cause internal bleeding and life-threatening complications.
Why is Ectopic Pregnancy Dangerous?
In a normal pregnancy, the egg travels to the uterus and implants itself safely. But in an ectopic pregnancy, it gets stuck outside the uterus, most often in a fallopian tube.
The growing embryo may rupture the tube, causing:
- Severe internal bleeding
- Damage to nearby organs
- Threat to the mother’s life
Here, early diagnosis is critical to avoid complications.
Early Signs and Symptoms
Early symptoms often mimic normal pregnancy, but some are red flags you shouldn’t ignore.
✅ Common Early Symptoms:
- Missed period
- Positive pregnancy test
- Breast tenderness
- Mild cramping
❗Warning Signs:
- Sharp or stabbing pain (usually on one side of the abdomen)
- Vaginal bleeding (light or heavy)
- Dizziness or fainting
- Shoulder pain (caused by internal bleeding irritating the diaphragm)
- Rectal pressure or discomfort during urination or bowel movements
If you experience any of these signs, seek emergency medical help immediately.
What Causes Ectopic Pregnancy?
Several conditions can cause or increase the risk of an ectopic pregnancy.
Common Causes:
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
- Sexually transmitted infections (like chlamydia or gonorrhea)
- Scarring from previous surgery or ectopic pregnancy
- Endometriosis
- Tubal ligation or sterilization
- Fertility treatments (like IVF)
- Smoking
How is it diagnosed?
Doctors use a combination of tests to confirm ectopic pregnancy.
- Blood tests: Measure levels of the pregnancy hormone hCG. If it’s rising abnormally, it could signal a problem.
- Transvaginal ultrasound: Helps locate where the embryo has implanted.
- Pelvic exam: Detects tenderness or masses near the ovaries or tubes.
Treatment Options
1. Medication (Methotrexate)
If caught early, doctors may prescribe methotrexate, a drug that stops the growth of the embryo. Your body will absorb the tissue naturally.
This method:
- Avoids surgery
- Requires follow-up blood tests to ensure hCG drops to zero
2. Surgery
If the pregnancy has advanced or ruptured, surgery is required.
- Laparoscopy: Minimally invasive procedure to remove the ectopic pregnancy
- Salpingectomy: Removal of the affected fallopian tube
- Salpingostomy: Removes the embryo but leaves the tube intact
Your doctor will choose the safest option depending on your condition.
Can I Get Pregnant Again After Ectopic Pregnancy?
Yes! Many women go on to have successful pregnancies after an ectopic.
However:
- If a tube was removed, your fertility may decrease.
- You may need IVF if both tubes are damaged.
- Future pregnancies should be monitored early to ensure proper implantation.
Consult a fertility specialist if you’re trying to conceive after an ectopic pregnancy.
How to Prevent Ectopic Pregnancy?
While not all cases can be prevented, you can lower your risk.
Prevention Tips:
- Treat STIs early and completely
- Avoid smoking
- Maintain good reproductive hygiene
- Get regular gynecological checkups
- Discuss your medical history with your doctor
Ectopic Pregnancy Facts & Statistics
- Happens in about 1 out of every 50 pregnancies
- 95% occur in the fallopian tubes
- Leading cause of maternal death in the first trimester
- Early treatment leads to full recovery in most cases
FAQs About Ectopic Pregnancy
Q: Can ectopic pregnancies be detected at home?
A: No. A pregnancy test may be positive, but only medical imaging and blood tests can confirm an ectopic pregnancy.
Q: How soon can it be diagnosed?
A: Usually between 4–6 weeks of pregnancy.
Q: Is it the same as a miscarriage?
A: No. A miscarriage occurs when a pregnancy fails naturally. Ectopic pregnancy is a medical emergency requiring intervention.
Q: Can it be prevented?
A: You can reduce risk but not always prevent it. Early diagnosis is key.
Q: How long can it go unnoticed?
A: An ectopic pregnancy can go unnoticed for up to 6 to 8 weeks. In the early stages, symptoms may be mild or mistaken for a normal pregnancy. However, as the embryo grows, it can cause severe pain, internal bleeding, or rupture of the fallopian tube. That’s why early prenatal check-ups and ultrasound scans are essential to detect and treat ectopic pregnancies before complications arise.
Final Thoughts
This pregnancy is a medical emergency, but with early detection and proper care, it can be treated effectively. Always pay attention to your body and never ignore unusual symptoms in early pregnancy.
If you’re pregnant and something doesn’t feel right, seek help immediately.
Related Resources:
- Very Early Signs of Pregnancy 1 Week
- Implantation Bleeding vs Period
- When to Take a Pregnancy Test
- Pregnancy Calculator
About the Author
A new father and founder of PregnancyKit, a health blog designed to help women understand early pregnancy signs, complications, and safe motherhood. Inspired by real-life struggles and guided by empathy, he writes to inform and support.